SLU Study Explores the Pandemic’s Impact on Breastfeeding Practices in Historically Marginalized Communities
11/14/2024
COVID-19 Provided the Elements for an Organic Experiment, Researchers Say
ST. LOUIS — A Saint Louis University study explored the impact of COVID-19 stay-at-home orders on breastfeeding practices in the U.S.
The study, recently published in the Maternal and Child Health Journal, provides critical insights into how pandemic-induced changes affected breastfeeding habits.

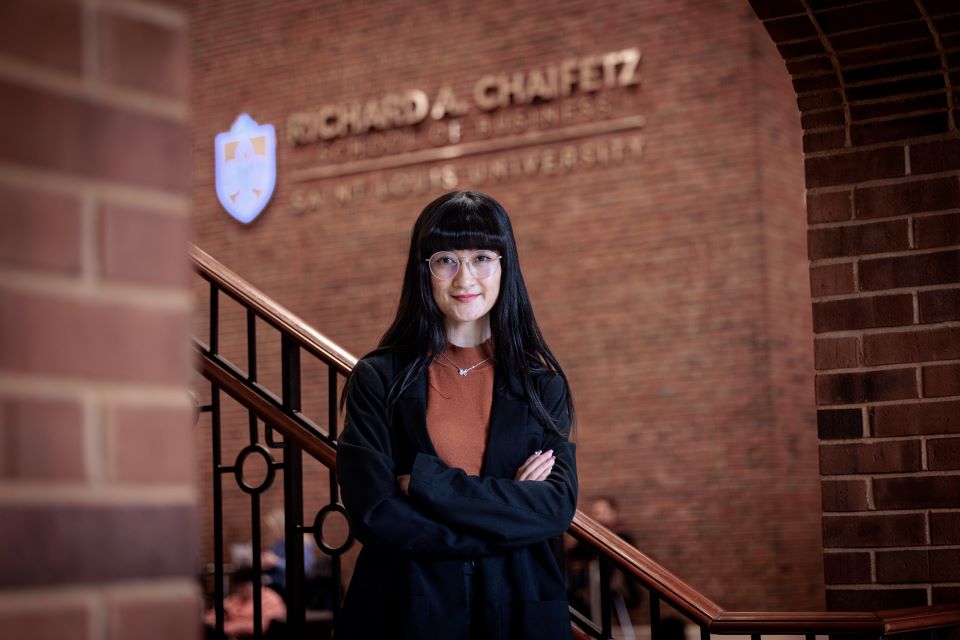
María José Romo-Palafox, Ph.D. SLU file photo.
Thirty-four percent of mothers said stay-at-home orders facilitated easier breastfeeding at home, stronger mother-child bonding, and extended breastfeeding duration for many women. However, the pandemic also presented significant barriers, including limited access to lactation support and heightened maternal stress.
Earlier studies on mothers' breastfeeding habits yielded samples of a majority of White, non-Hispanic, well-educated, partnered, and employed respondents. This study surveyed the breastfeeding practices of a large and diverse sample of U.S. mothers across various regions, income levels, and racial/ethnic backgrounds.
María José Romo-Palafox, Ph.D., assistant professor of nutrition and dietetics at SLU, is the paper’s senior author. Romo-Palafox is a registered dietitian and researcher focusing on maternal-child health in historically marginalized communities.
“As a Mexican immigrant, I am dedicated to addressing the systemic barriers that disproportionately affect breastfeeding and maternal health. Observing the pandemic's impact on breastfeeding illuminated the urgent need for holistic, supportive work policies,” she said. “I am passionate about contributing to solutions that support breastfeeding and provide mental health and financial stability resources for mothers, creating healthier outcomes for both mothers and children across diverse backgrounds.”
Breastfeeding is one of the best investments in a child’s health, laying a solid nutritional foundation early in life. The World Health Organization recommends exclusively breastfeeding infants up to six months of age; however, in the U.S., only 26% of infants met this recommendation in 2020.
Returning to work has emerged as one of the main barriers to exclusive and continued breastfeeding. Women attempting to continue breastfeeding by pumping at work often find it challenging to meet their goals due to incomplete support from their management and organization, such as the lack of a designated lactation space and limited time to pump.
The U.S. Senate passed the Providing Urgent Maternal Protections (PUMP) for Nursing Mothers Act in December 2022 and the Pregnant Workers Fairness Act.
While valuable, Romo-Palafox and her team argue that existing policies like the PUMP Act and Pregnant Workers Fairness Act may not adequately meet the needs of low-income, racially diverse mothers who often return to work early out of financial necessity. The COVID-19 stay-at-home orders provided a unique natural experiment where many women found that working from home allowed for more sustained breastfeeding and promoted stronger mother-infant bonding—this period highlighted that even with current policies, many mothers particularly those from historically marginalized backgrounds—require more comprehensive support beyond the lactation accommodation alone.
Romo-Palafox and her team propose policies that go beyond current mandates by ensuring flexibility in work location, especially for roles that typically require in-person attendance. Additionally, policies should include expanded financial stability and mental health resources alongside telehealth lactation services.
“For instance, offering telehealth options for lactation consultants through programs like WIC, which proved effective during the pandemic, is essential to maintain. Although many programs temporarily offered these flexible services, they have since reduced access, leaving gaps in support,” she said. “Reinstating and standardizing telehealth lactation services for breastfeeding mothers, particularly through WIC, would enhance breastfeeding success, reduce stress, and better address the unique challenges faced by low-income and diverse populations.”
Other authors include Valerie Graham, Department of Nutrition and Dietetics, Saint Louis University; Haley Pritz, Department of Nutrition and Dietetics, Saint Louis University; and Zoe Henkes, Saint Louis University School of Medicine.
Latest Newslink
- Why Do Raccoons Cross the Road? SLU, St. Louis Zoo Research Shows They Don'tA new study led by researchers from Saint Louis University, the Saint Louis Zoo, and partner organizations set out to understand how raccoons use space in one of the nation's largest urban parks.
- Structurally Sound: Two Gingerbread Houses Built by SSE Students Hold Up Under 100-Plus Pounds of WeightTeams of students, faculty and staff in Saint Louis University's School of Science and Engineering recently put their engineering skills to work for a December Innovation Challenge, building gingerbread houses designed to stand up during a weight-loading competition.
- Saint Louis University Student Speaks at Ignatian Family Teach-In for JusticeSaint Louis University senior Sahar Hussaini shared her views on fast consumerism and why she believes in Catholic Ethical Purchasing at the 2025 Ignatian Family Teach-In for Justice. The event, held annually in Washington, D.C., is the nation’s largest Catholic social justice advocacy day.
- SLU Commits up to $1.5 Million to Support Local Students Pursuing Social Work and Criminal Justice CareersThe new initiative — representing a commitment of up to $1.5 million in scholarship support over the next several years — is designed to strengthen the region’s social work and criminal justice workforce by expanding college access for talented local students.
- University Core Honors Ignite Seminar InstructorsTwo Ignite Seminar instructors have been recognized with the 2025 Ignite Instructor of the Year Award. At a ceremony Tuesday night in Cupples House, Carolyn O'Laughlin, Ph.D. (Education) and Amanda Barton, Ph.D. (RISE Counselor) were honored by the University Core after being nominated by students in their Ignite Seminars.
- Sharing Throughout the Season: Ways to Give Back at SLUThis holiday season, Saint Louis University is highlighting organizations that could benefit from the gift of time or donations, including the University's annual Blue Santa toy drive.