SLU Researchers Enroll Participants in 2-in-1 COVID and Flu Vaccine Clinical Trial
ST. LOUIS – Saint Louis University’s Center for Vaccine Development is participating in a clinical study for an investigational vaccine being developed against influenza and COVID developed by Pfizer, which is funding this research.
While there are licensed vaccines and treatments for both influenza and COVID, the current vaccines have been given as separate shots. This study looks at whether both vaccines can be combined into one shot without affecting the antibody response to either vaccine.

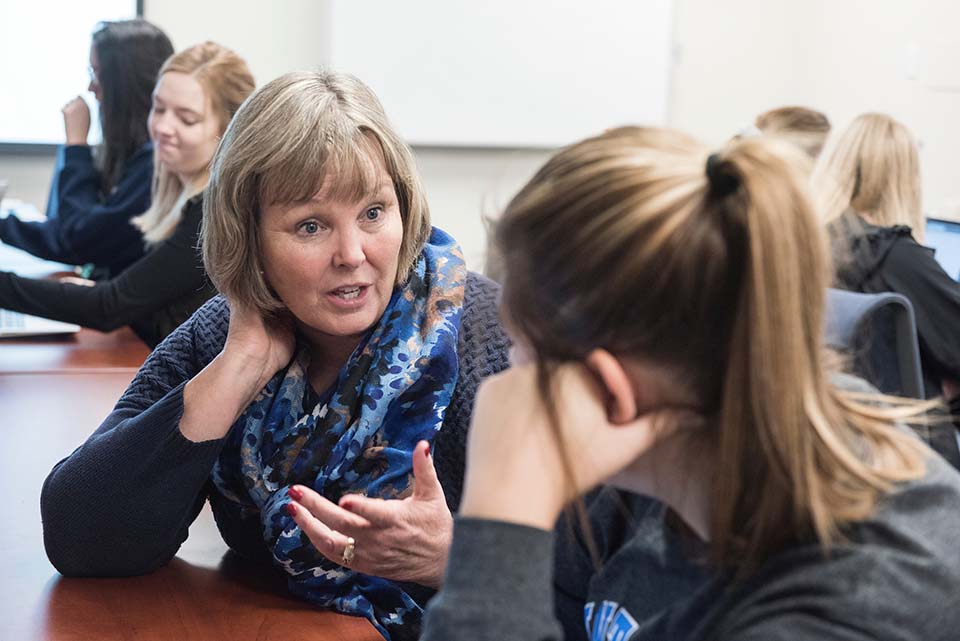
Sarah George, M.D., professor of infectious diseases at SLU School of Medicine and a researcher in SLU’s Vaccine Center. SLU file photo.
Sarah George, M.D., professor of infectious diseases at SLU School of Medicine and a researcher in SLU’s Vaccine Center, will assist in studying whether the combined vaccine induces the body to make antibodies to both influenza and COVID, compared with giving both vaccines separately.
“Since it looks like COVID will be with us for the long haul, just as flu is, it’s important to see if we can combine both vaccines into one shot without compromising immunity of both,” George said. “It’s vital that we continue to work to develop combined vaccines that can protect all of us, especially the vulnerable, from these illnesses.”
The phase 3 clinical trial is being conducted at over 200 sites in the United States, including Saint Louis University. SLU researchers are recruiting around 150 healthy adults 18 through 64 years of age who have not had a flu or COVID vaccine in the past 6 months. Overall, the study will recruit 9,000 volunteers and will last about a year. Each volunteer will have 3 study visits.
To learn more about vaccine research being conducted at Saint Louis University, call 314-977-6333 or email vaccine@slu.edu. For more information on this study, please visit the ClinicalTrials.gov website link here.
Latest Newslink
- Kathryn Mitchell Pierce, Ph.D.: 1955-2025Kathryn Mitchell Pierce, Ph.D., associate professor of educational studies, died Wednesday, Dec. 10, 2025. She was 70 years old. Pierce joined Saint Louis University in 2015 as an assistant professor in the School of Education. Initially a literacy specialist in the undergraduate program, she eventually taught and mentored across all levels at the School of Education. She became an associate professor in 2022.
- Saint Louis University Student Speaks About Leadership and Disability at Ignatian Family Teach-In for JusticeSaint Louis University senior Grace LoPiccolo shared her personal leadership journey at the 2025 Ignatian Family Teach-In for Justice. The event, held annually in Washington, D.C., is the nation’s largest Catholic social justice advocacy day.
- SLU Research Shows Surge in Alcohol-Related Liver Disease Driving ‘Deaths of Despair’Researchers at Saint Louis University School of Medicine say deaths from alcohol-related liver disease have surged in recent years, and the increase is hitting people without a college degree the hardest. While nearly every demographic group is seeing higher death rates—including those with college degrees—the gap between economically disadvantaged groups and more affluent ones is growing, according to new research.
- Saint Louis University Joins Multi-Disciplinary Research Team to Enhance Stress Resilience in SorghumSaint Louis University is part of a multi-disciplinary team, led by the Donald Danforth Plant Science Center, to deepen the understanding of sorghum, a versatile bioenergy crop, and its response to environmental challenges.The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Biological and Environmental Research (BER) program supports the three-year $2.5 million project for Genomics-Enabled Understanding and Advancing Knowledge on Plant Gene Function. Saint Louis University will receive $437,039 for its portion of the study.
- SLU Graduates Celebrated at Midyear CommencementSaint Louis University celebrated its Midyear Commencement on Saturday, Dec. 13, inside Chaifetz Arena. More than 1,900 guests watched as 600-plus SLU students walked across the stage and left as graduates.
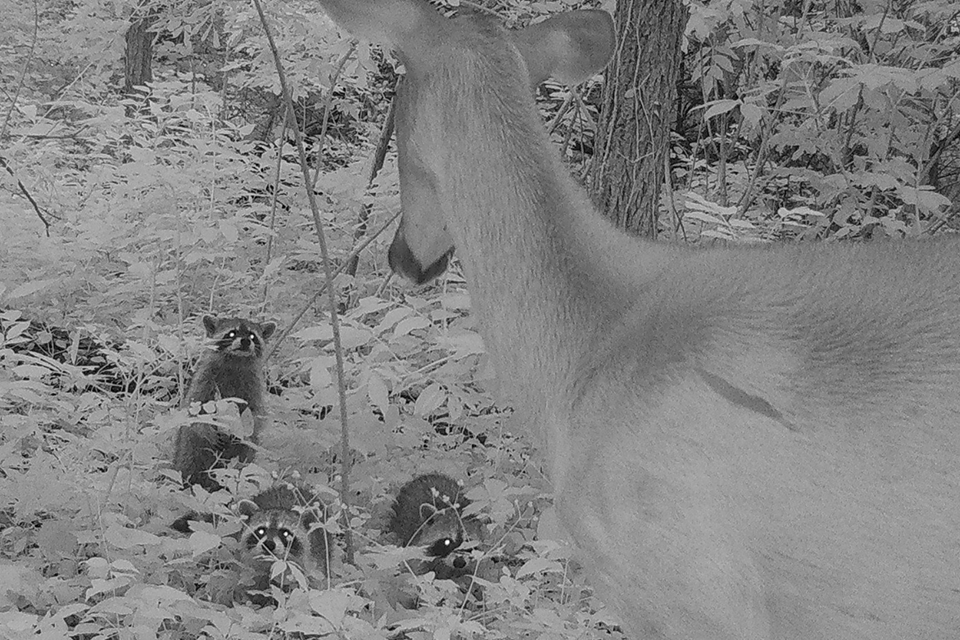
- Why Do Raccoons Cross the Road? SLU, St. Louis Zoo Research Shows They Don'tA new study led by researchers from Saint Louis University, the Saint Louis Zoo, and partner organizations set out to understand how raccoons use space in one of the nation's largest urban parks.