SLU Researchers Identify Sex-Based Differences in Immune Responses Against Tumors
Researchers at Saint Louis University School of Medicine investigated differences in T-cell responses between male and female patients with lung cancer that may help direct future treatments. T-cell responses are part of the adaptive immune system, part of the body’s “smart system” that monitors for threats and fights them with customized defenses.
"Therapies that use the patient's immune system to fight their disease have a lot of potential to change how patients are treated. However, one of the biggest problems in the field right now is that these immunotherapies work well only in a small fraction of patients," Elise Alspach, Ph.D., assistant professor of molecular microbiology and immunology at SLU, senior author on the paper.

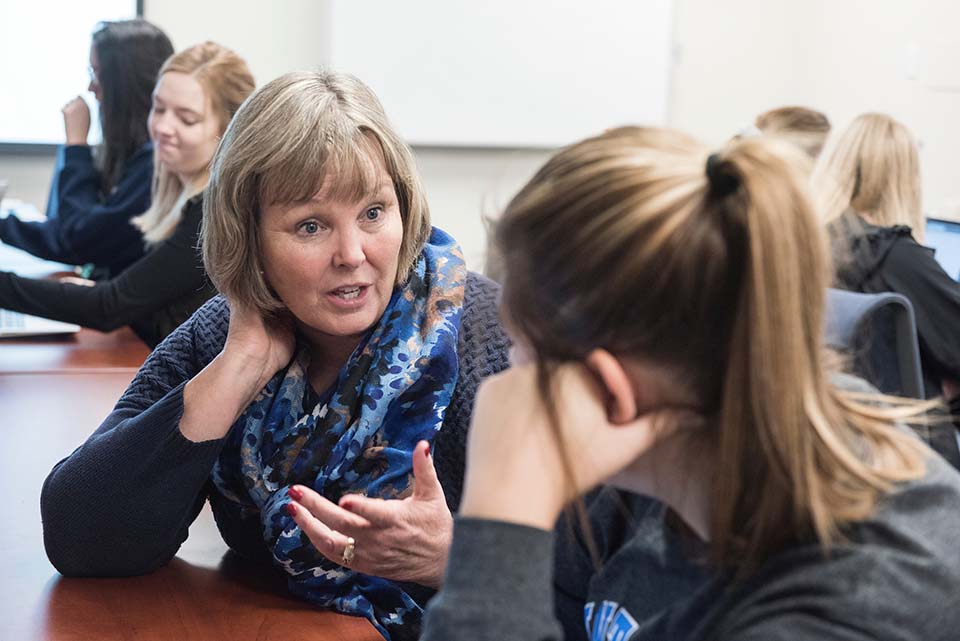
Elise Alspach, Ph.D., assistant professor of molecular microbiology and immunology, and her team identify sex-based differences in immune responses against tumors. Photo by Sarah Conroy.
Alspach and her team aimed to understand what determines good T-cell responses in patients, why some patients seem to have better T-cell responses than others, and why some patients respond well to immunotherapies. Research findings recently published in Cancer Immunology Research show that a protein called CXCL13 that has recently been linked to immunotherapy response in patients is more highly expressed in females than males. Additionally, Alspach and her team found that CXCL13 expression is a better marker of immunotherapy response in females than in males.

Elise Alspach, Ph.D., conducts research in a lab at Saint Louis University. Photo by Sarah Conroy.
Alspach and her team used single-cell RNA sequencing in human datasets to understand more about differences in how male and female immune systems respond to tumors. Single-cell RNA sequencing allows scientists to learn what’s happening inside individual cells. Using this technology, Alspach and her team determined that T-cells that infiltrate female tumors are highly activated and ready to identify tumor cells and kill them. They also noted immune suppressive T-cells present more frequently in male tumors than in female tumors.
Alspach and her team discovered that there is growing evidence that the male sex is associated with a better response to immunotherapy, which she said appears to contrast with their work and recently published papers showing that females mount stronger immune responses against their tumors.
"We currently don’t understand why males would respond better than females to immune targeting therapies, but this interesting juxtaposition highlights the need for more research into the variable of sex in the immune response against cancer," Alspach said.
Alspach said the potential of immunotherapy is revolutionary as it mediates tumor rejection in patients and induces long-term remission.
"When we get infected with a virus, the immune system generates a population of cells that can remember that virus and do a better job of eliminating it from your body, so the immune system does the same thing against tumors,” she said. “The memory response against that tumor partly generates long-term remissions that we see in patients treated with immunotherapies."
Before the advent of immunotherapies, Alspach said cancer treatments were hard on the body and not tumor-specific or, in the case of small molecule drugs that targeted specific proteins inside tumor cells, frequently become resistant to therapies. Current immunotherapies are typically much better tolerated in more patients, and patients can maintain a higher quality of life because the immune system can be educated to specifically target the tumor rather than all the tissues in the body.
Because immune responses against tumors are different between the sexes, Alspach and her colleagues concluded that it makes sense to potentially design different treatments for male versus female patients. In the future, she hopes more appropriate therapeutic strategies will be devised to target the pathways that mediate better tumor control in ways that benefit individual patients.
This research was possible thanks to a recent investment in single-cell RNA sequencing technology at Saint Louis University, allowing researchers to bring us closer to new cures.
Additional authors include Richard J. DiPaolo, Ph.D.; Ryan M. Teague, Ph.D.; Michelle Brennan, Ph.D.; David DeBruin; Chinye Nwokolo; Katey S. Hunt; Alexander Piening; Maureen J. Donlin; and Stephen T. Ferris, Department of Molecular Microbiology and Immunology, Saint Louis University School of Medicine.
Latest Newslink
- Kathryn Mitchell Pierce, Ph.D.: 1955-2025Kathryn Mitchell Pierce, Ph.D., associate professor of educational studies, died Wednesday, Dec. 10, 2025. She was 70 years old. Pierce joined Saint Louis University in 2015 as an assistant professor in the School of Education. Initially a literacy specialist in the undergraduate program, she eventually taught and mentored across all levels at the School of Education. She became an associate professor in 2022.
- Saint Louis University Student Speaks About Leadership and Disability at Ignatian Family Teach-In for JusticeSaint Louis University senior Grace LoPiccolo shared her personal leadership journey at the 2025 Ignatian Family Teach-In for Justice. The event, held annually in Washington, D.C., is the nation’s largest Catholic social justice advocacy day.
- SLU Research Shows Surge in Alcohol-Related Liver Disease Driving ‘Deaths of Despair’Researchers at Saint Louis University School of Medicine say deaths from alcohol-related liver disease have surged in recent years, and the increase is hitting people without a college degree the hardest. While nearly every demographic group is seeing higher death rates—including those with college degrees—the gap between economically disadvantaged groups and more affluent ones is growing, according to new research.
- Saint Louis University Joins Multi-Disciplinary Research Team to Enhance Stress Resilience in SorghumSaint Louis University is part of a multi-disciplinary team, led by the Donald Danforth Plant Science Center, to deepen the understanding of sorghum, a versatile bioenergy crop, and its response to environmental challenges.The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Biological and Environmental Research (BER) program supports the three-year $2.5 million project for Genomics-Enabled Understanding and Advancing Knowledge on Plant Gene Function. Saint Louis University will receive $437,039 for its portion of the study.
- SLU Graduates Celebrated at Midyear CommencementSaint Louis University celebrated its Midyear Commencement on Saturday, Dec. 13, inside Chaifetz Arena. More than 1,900 guests watched as 600-plus SLU students walked across the stage and left as graduates.
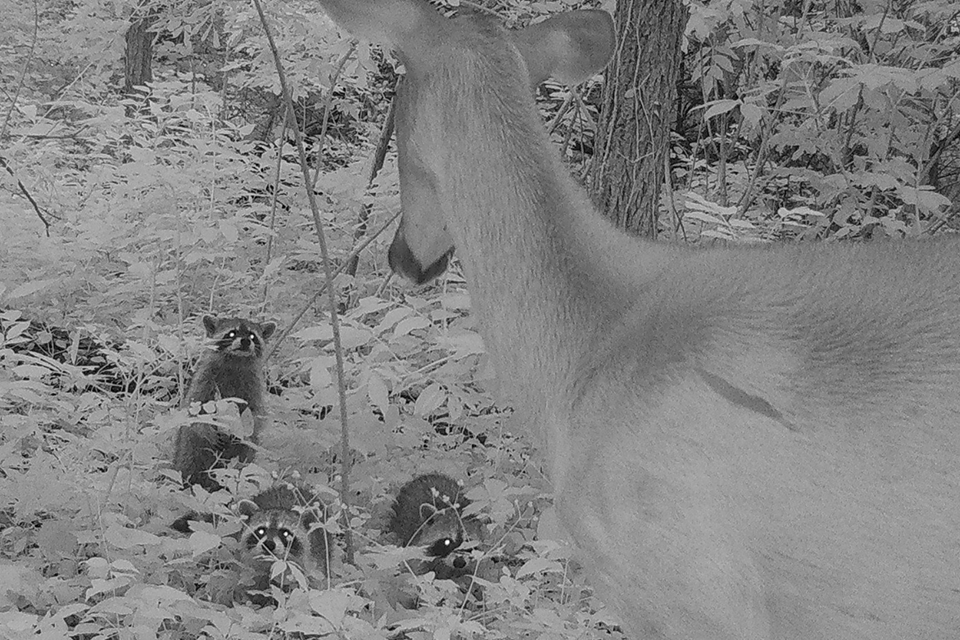
- Why Do Raccoons Cross the Road? SLU, St. Louis Zoo Research Shows They Don'tA new study led by researchers from Saint Louis University, the Saint Louis Zoo, and partner organizations set out to understand how raccoons use space in one of the nation's largest urban parks.