Cult Mentality: SLU Professor Makes Monumental Discovery in Italy
Douglas Boin, Ph.D., a professor of history at Saint Louis University, made a major announcement at the annual meeting of the Archeological Institute of America, revealing he and his team discovered what they believe to be an ancient Roman temple that adds significant insights into the social change from pagan gods to Christianity within the Roman Empire.
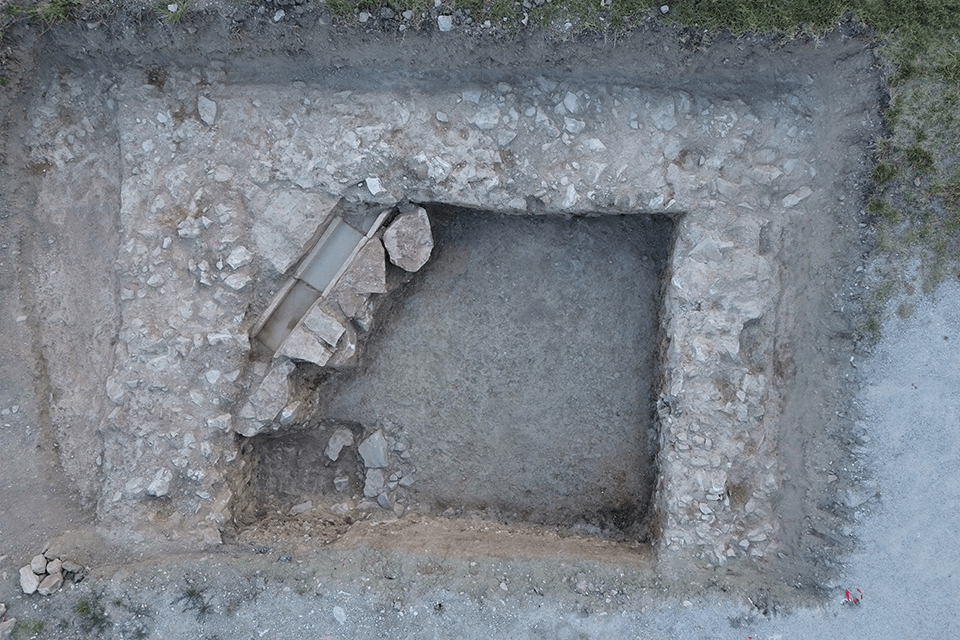

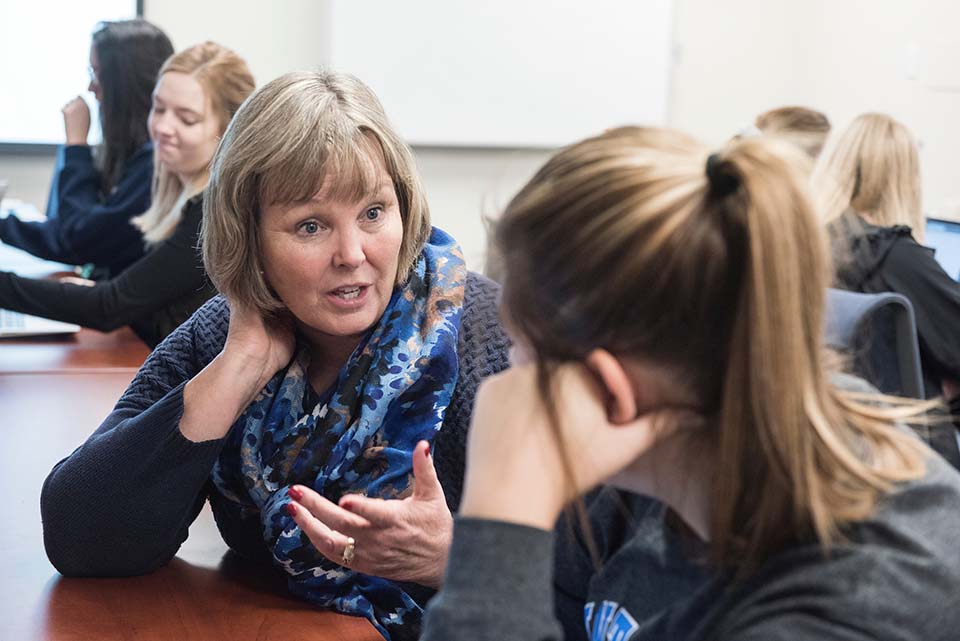
An aerial photo of what Douglas Boin, Ph.D., believes to be the inside walls of an Imperial Cult temple. This temple immediately became what Boin calls the largest evidence ever of the Imperial Cult in both fourth-century Italy and the late Roman Empire. Photo by Luca Primavesi, Spello Project.
“We found three walls of a monumental structure that evidence suggests belonged to a Roman temple that dates to Constantine's period,” Boin said. “It dates to the fourth century AD and if our team’s hypothesis is right, it will be a remarkable addition to the landscape of this corner of Italy. It will significantly aid in the understanding of the ancient town, the ancient townscape and city society in the later Roman Empire because it potentially shows the continuities between the classical pagan world and early Christian Roman world that often get blurred out or written out of the sweeping historical narratives.”
Boin, Dr. Letizia Ceccarelli, Politecnico di Milano, and the rest of the excavation team made the discovery over the summer. Boin, an expert in ancient Roman and its religious transitions, had been digging in the town of Spello, the famous medieval hilltop city about 20 minutes from Assisi and 2.5 hours north of Rome. Boin selected the town based on a rescript of a 4th century letter from Emperor Constantine to the townspeople regarding a religious holiday.
This rescript, which was discovered in the 18th century, allowed the people of Spello to celebrate a religious festival in their hometown rather than travel a great distance to another festival. However, in order to do so, the town was told it must erect a temple to Constantine’s divine ancestors, the Flavian family, and worship them, showcasing how multicultural Roman society was at the time.
“There was a remarkable religious continuity between the Roman world and the early Christian world,” Boin said. “Things didn't change overnight. Before our find, we never began to imagine the size of the actual physical, religious sites that could be associated with this late ‘imperial cult practice.’ The location of this temple had never been securely identified, but because of the inscription and its reference to a temple, Spello offered a very tantalizing potential for a major discovery of an Imperial cult underneath a Christian ruler.”
Boin traveled to Spello and oversaw underground imaging to determine if there were any potential ruins below the surface that needed to be uncovered. After many weeks, and almost by chance, Boin finally received promising images underneath a parking lot where monumental foundations were suspected to be.
Very carefully, the team dug into the ground until they found two adjoining walls. More digging unearthed what Boin believes to be the inside walls of the temple. Another season of work will be required to gather additional, supporting data and further test the team’s hypothesis, but if it holds, this temple would immediately become what Boin calls the largest evidence ever of the Imperial Cult in both fourth-century Italy and the late Roman Empire.
“There's evidence from other places throughout the Roman world that Christian rulers supported imperial cult practices,” Boin said. “We've known that pagans worshiped at their temples in the fourth century, but those findings have all been small and inconsequential. And we've known that Christians supported the imperial cult, and we’ve known that without any sense of where it would have happened. This perceived temple would bridge those two landmarks, and in that respect, it is unlike any temple that I know about from the Mediterranean world of the fourth century Roman Empire. Any study of the imperial cult in the fourth century Roman Empire is now going to have to take account of this temple, which is an incredible discovery to make.”
With the discovery, Boin now can show how the societal changes of the time moved very slowly. Though Constantine was the first Roman emperor to famously convert to Christianity, it would take almost 70 years for Christianity to become the official religion of the Roman Empire, under the Emperor Theodosius. During that time it still took many convincing and gradual shifts for those who worshiped pagan gods to convert to Christianity.
“This changes how we perceive the pace of social change and our impression of the impact of social and cultural change,” Boin said. “This building, in a very radical way on its own, shows us the staying power of the pagan traditions that had been on the ground for centuries prior to the rise of Christianity, and it shows us how the Roman emperors continued to negotiate their own values, their own hopes and dreams for the future of the emperor and the Empire without knocking down or burying the past.”
Still, even after discovering three inner walls of a monumental structure, Boin is cautious about the finds, emphasizing that there is much that remains unknown and more discoveries to make. Boin and his team will return to Spello next summer to fully excavate the area to examine the ruins and whatever else lies beneath the dirt, where he hopes to make even more significant discoveries.
“We are on the cusp of giving people a very visible piece of evidence that really upends the neat and tidy ways people think about big moments of cultural change, but there is still plenty of work to be done,” Boin said “Cultural changes are never as big as we think they are when living through them, and there’s a lot of gray area in between people’s customs and the broader society and culture. And a lot of those can be left out of the story. So to have this temple potentially be a temple dedicated to Constantice’s divine ancestors as a way to worship the emperor in an increasingly Christian world at the time, it’s so weird and I love that we can bring it to light. I can’t wait to find out what more we can uncover with our next digs.”
Latest Newslink
- Kathryn Mitchell Pierce, Ph.D.: 1955-2025Kathryn Mitchell Pierce, Ph.D., associate professor of educational studies, died Wednesday, Dec. 10, 2025. She was 70 years old. Pierce joined Saint Louis University in 2015 as an assistant professor in the School of Education. Initially a literacy specialist in the undergraduate program, she eventually taught and mentored across all levels at the School of Education. She became an associate professor in 2022.
- Saint Louis University Student Speaks About Leadership and Disability at Ignatian Family Teach-In for JusticeSaint Louis University senior Grace LoPiccolo shared her personal leadership journey at the 2025 Ignatian Family Teach-In for Justice. The event, held annually in Washington, D.C., is the nation’s largest Catholic social justice advocacy day.
- SLU Research Shows Surge in Alcohol-Related Liver Disease Driving ‘Deaths of Despair’Researchers at Saint Louis University School of Medicine say deaths from alcohol-related liver disease have surged in recent years, and the increase is hitting people without a college degree the hardest. While nearly every demographic group is seeing higher death rates—including those with college degrees—the gap between economically disadvantaged groups and more affluent ones is growing, according to new research.
- Saint Louis University Joins Multi-Disciplinary Research Team to Enhance Stress Resilience in SorghumSaint Louis University is part of a multi-disciplinary team, led by the Donald Danforth Plant Science Center, to deepen the understanding of sorghum, a versatile bioenergy crop, and its response to environmental challenges.The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Biological and Environmental Research (BER) program supports the three-year $2.5 million project for Genomics-Enabled Understanding and Advancing Knowledge on Plant Gene Function. Saint Louis University will receive $437,039 for its portion of the study.
- SLU Graduates Celebrated at Midyear CommencementSaint Louis University celebrated its Midyear Commencement on Saturday, Dec. 13, inside Chaifetz Arena. More than 1,900 guests watched as 600-plus SLU students walked across the stage and left as graduates.
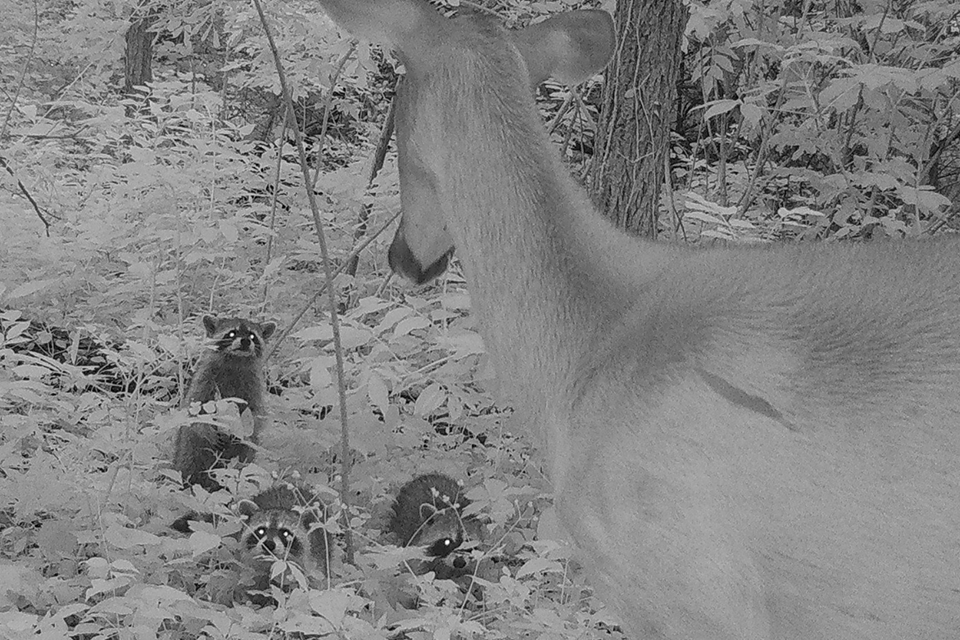
- Why Do Raccoons Cross the Road? SLU, St. Louis Zoo Research Shows They Don'tA new study led by researchers from Saint Louis University, the Saint Louis Zoo, and partner organizations set out to understand how raccoons use space in one of the nation's largest urban parks.